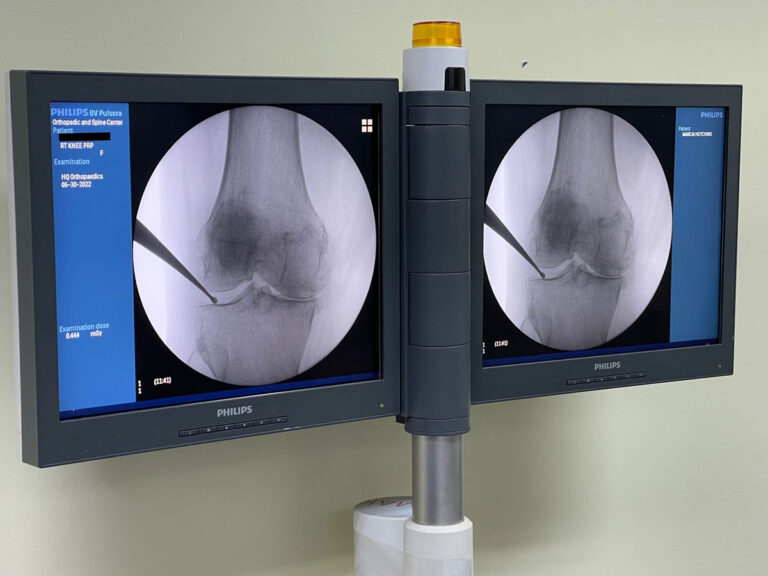
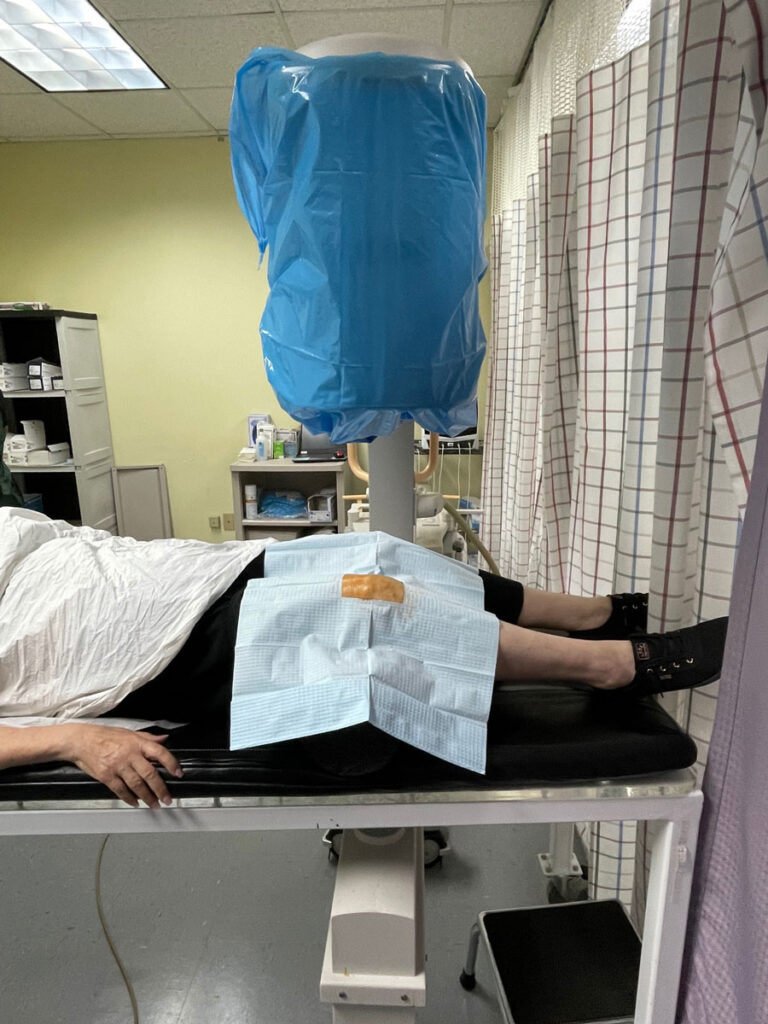
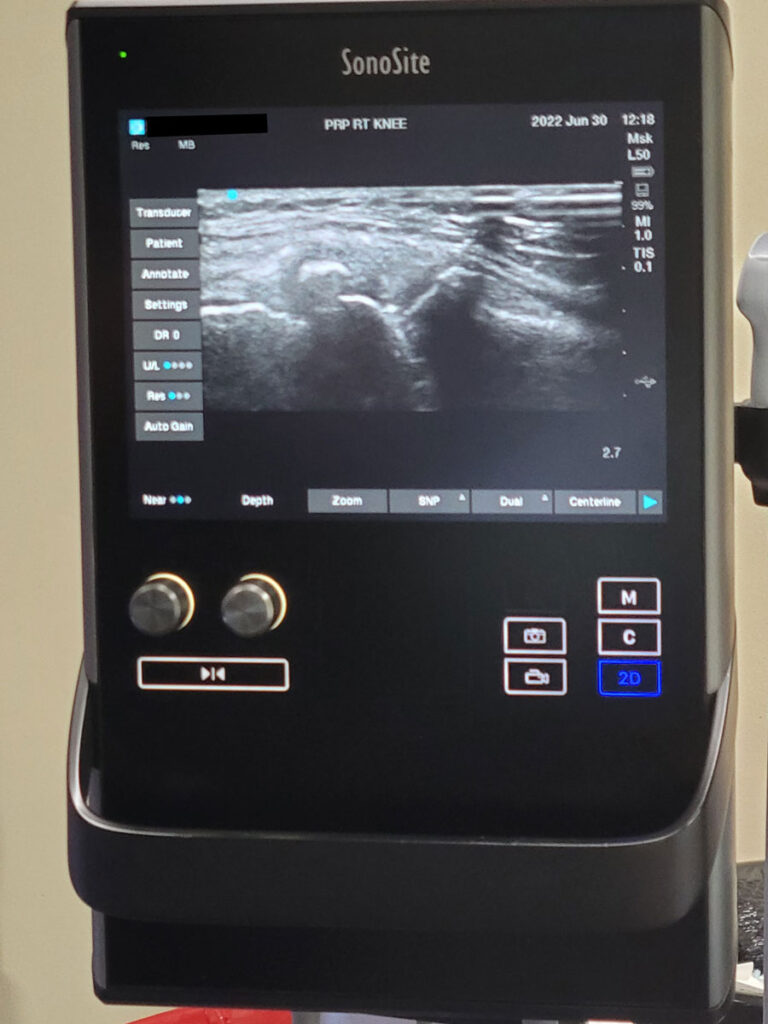
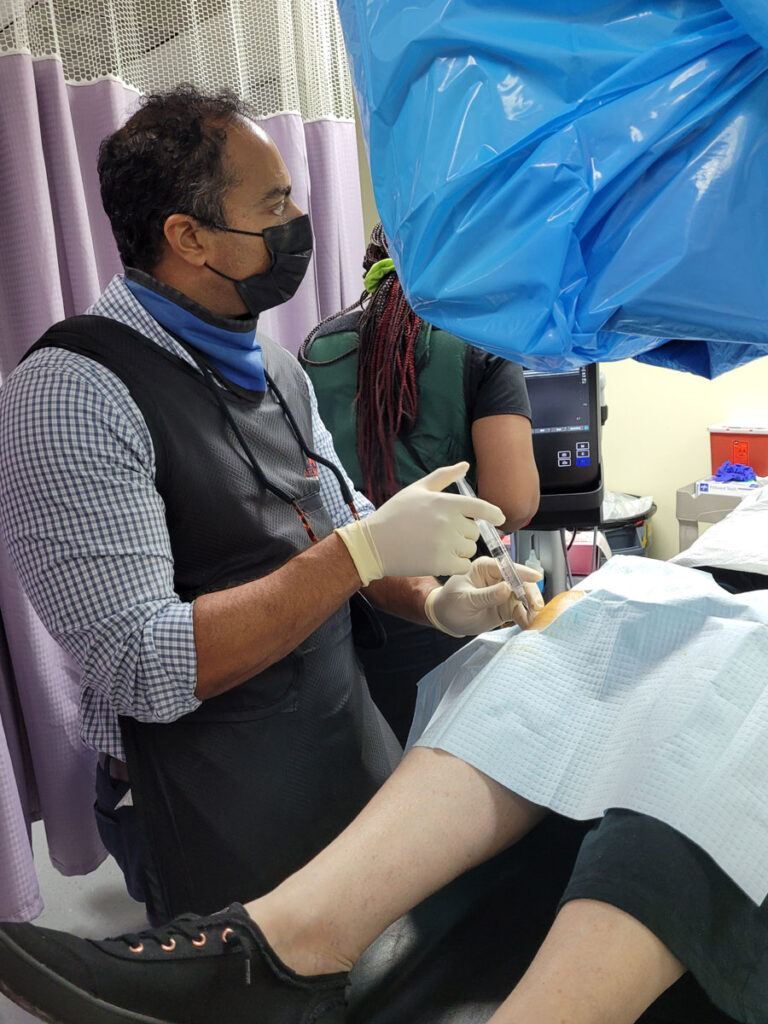
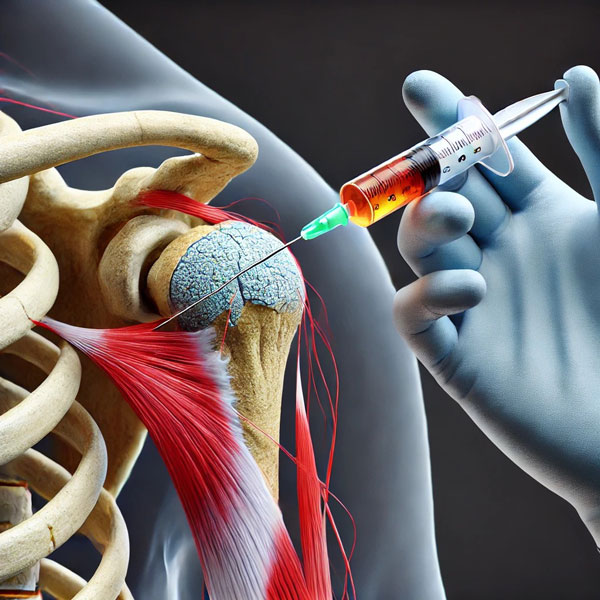
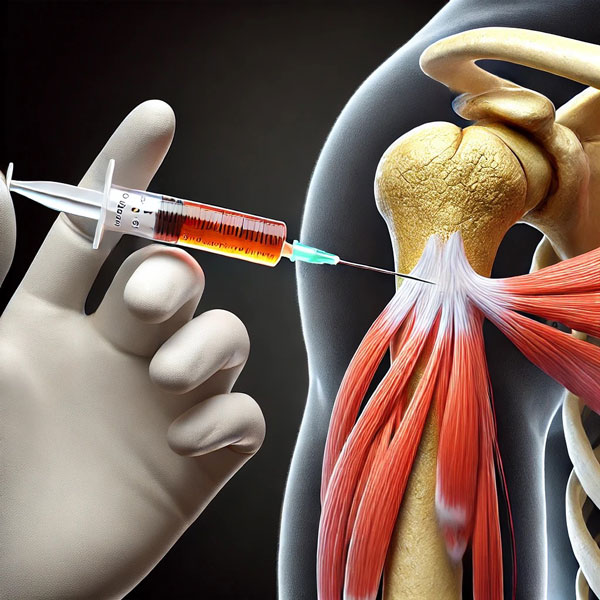
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a regenerative medicine treatment that utilizes a patient’s own blood to promote healing. The process involves drawing a small sample of blood, which is then centrifuged to concentrate platelets and growth factors.
These bioactive components are injected into the affected area, such as joints, tendons, or ligaments, to stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
PRP is widely used for musculoskeletal injuries, osteoarthritis, and even in aesthetic medicine for skin and hair regeneration
Regenerative medicine is an emerging field focused on restoring damaged tissues and organs through biological mechanisms that stimulate natural healing processes. It encompasses various techniques, including stem cell therapy, PRP, and tissue engineering, to enhance the body’s ability to repair itself. Unlike conventional treatments that primarily manage symptoms, regenerative medicine aims to address the root cause of tissue degeneration, making it a promising approach for conditions such as osteoarthritis, spinal cord injuries, and degenerative diseases.
PRP plays a significant role in regenerative medicine by leveraging the body’s natural healing potential. Growth factors within platelets accelerate tissue repair, modulate inflammation, and enhance cell proliferation.
This makes PRP an attractive alternative to invasive procedures, such as surgery, for conditions like knee osteoarthritis and tendon injuries. When combined with other regenerative techniques, PRP has the potential to improve outcomes by fostering a more biologically favorable environment for healing and long-term tissue regeneration.